As defines in ISO 857-1, MIG welding is a gas-shielded metal arc welding, which is the wire is melted and shielded by the gas. The ISO standard defines that the MIG welding use a wire where by gas from an external source surrounds the arc and the weld pool to protect them from the atmosphere.
The welding process characterised in that a wire electrode is always turn arround by the spool when the switch button on the welding torch is pressed. The spool can turn arround using a wire feed motor that powered by the contact tip so that the arc can burn between the end of the wire electrode and the metal.
The shielding gas will flows out of the shielding gas nozzle, which surrounds the wire electrode concentrically. This is the picture of MIG welding process with the nozzle structure.
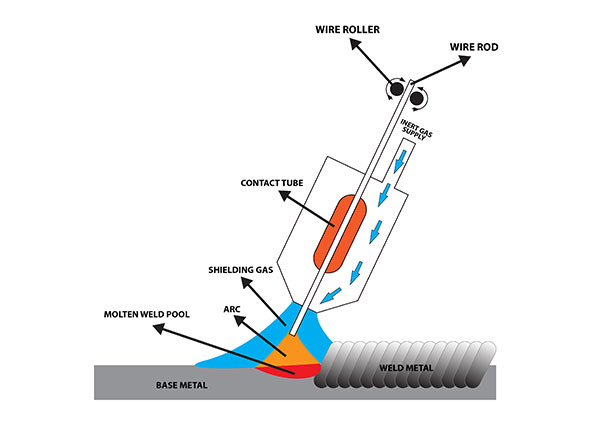
As you can see on that picture, after you pressed the torch’s switch the wire roller will move the wire electrode forward. The wire roller will continue roll while you press the torch’s switch. At the same time, the shielding gas begins to flow.
When the wire electrode touch the surface of the metal, a short circuit occurs. Owing to the high current density at the electrode’s tip, the metal start vaporising at the point of contact and the arc ignites, of course covered by the shielding gas.
The roller speed will affects the molten arc, so you have to adjust the wire speed or roller speed moves normally ( not to fast and not to slow ). The wire speed setting is affected by the value of amperage, voltage and the thickness of metal that you weld.
But newer types of MIG / MAG systems offer the automatic optional setting which is known as a wire creep speed. So you don’t have to manually set the wire speed while preparing you welding process. The wire speed will automatically set by the systems when you set the amperage and the voltage that you want to apply to your weld.
Torch Position
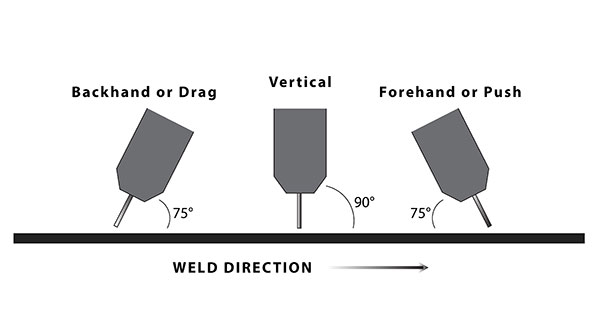
Besides having to consider the speed of the wire electrode, the amperages and voltages value. You also have to adjust the position of the welding torch while welding. The welding torch is tilted in the direction of welding by around 65° to 75° of the metal surface.
You can drag or push the torch while welding, so it doesn’t really affect the welding result by dragging or pushing the torch. And it’s distance of the wire tip to the metal’s surface should be 10 to 12 times the wire diameter.
Welding Parameters
You can weld normally with filler, final and backing runs on thicker panels, spray or long arcs are set with higher power range. And take a rest for a while because hottest metal make you produce bad welding. And for the thin metal, you can use a short arc or using a lower power range pulsed arc.
This welding tasks can also be performed with very low spatter using the pulsed arc. With pulsed welding, the display instruments show the arithmetic average value of the current and arc voltage produced in the pulse and base phase and base phase at the set pulse frequency.
You can use the welding table as guideline to produce a better welding result. If you feel need to learn about MMA / stick welding then click this link for a better experiences << MMA basic welding knowledge >>
